POODLE, which stands for “Padding Oracle on Downgraded Legacy Encryption”, is a vulnerability in SSL 3.0; the designation given to this CVE is CVE-2014-3566. An attacker can utilize weaknesses in how SSL 3.0 encrypts data to achieve access to user data. Although SSL 3.0 is now mostly considered deprecated, many servers still support the protocol because of its use as a legacy compatibility option and are, theoretically, still vulnerable to POODLE.
Addressing the SSL vulnerabilities becomes part of data security and ensuring users’ trust in their website for any website owner. This tutorial tries to outline what the SSL POODLE attack basically constitutes and how one can easily avoid it using various server environments. Apart from that, CertPanel’s SSL Monitor tool will be introduced; this will help to easily find and manage SSL vulnerabilities in the form of POODLE or similar vulnerabilities.
What is an SSL POODLE Attack?
The Padding Oracle on Downgraded Legacy Encryption, or POODLE, is an attack that uses weaknesses in the padding of SSL 3.0 to decrypt data sent over HTTPS. This vulnerability is critical to most websites still supporting protocol SSL 3.0, as it allows an attacker to intercept and decode encrypted information in transit. SSL/TLS security is important both in terms of prevention against man-in-the-middle attacks and for data privacy. It’s also recommended to disable SSL 3.0 and use stronger protocols such as TLS 1.2 and above to mitigate the POODLE vulnerability.
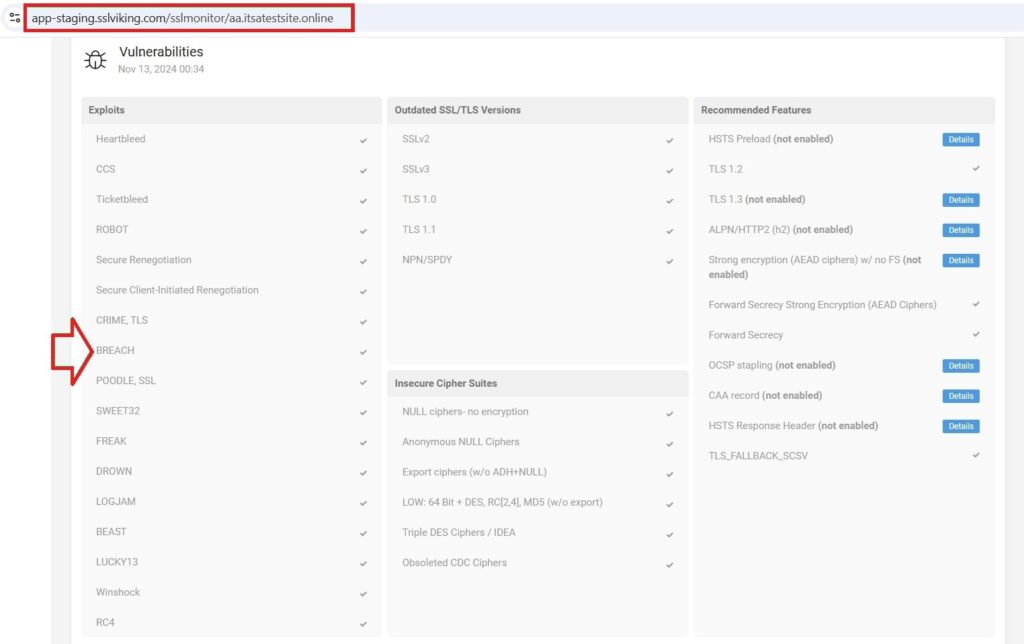
Detection of SSL POODLE Vulnerability Using CertPanel SSL Monitor
The CertPanel SSL Monitor will go a long way in effectively detecting vulnerabilities like POODLE on your website. This tool does constant monitoring of the setup of SSL/TLS on your site and informs you about potential weaknesses in security.
Here is how you will detect the SSL POODLE vulnerability using the CertPanel SSL Monitor:
- Sign up for the CertPanel SSL Monitor: You should navigate to the product page at https://certpanel.com/ to learn more about features and benefits, as well as the pricing.
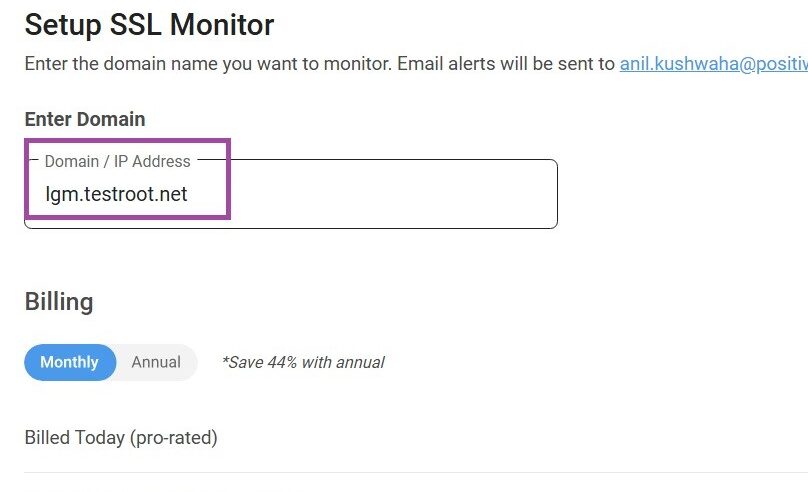
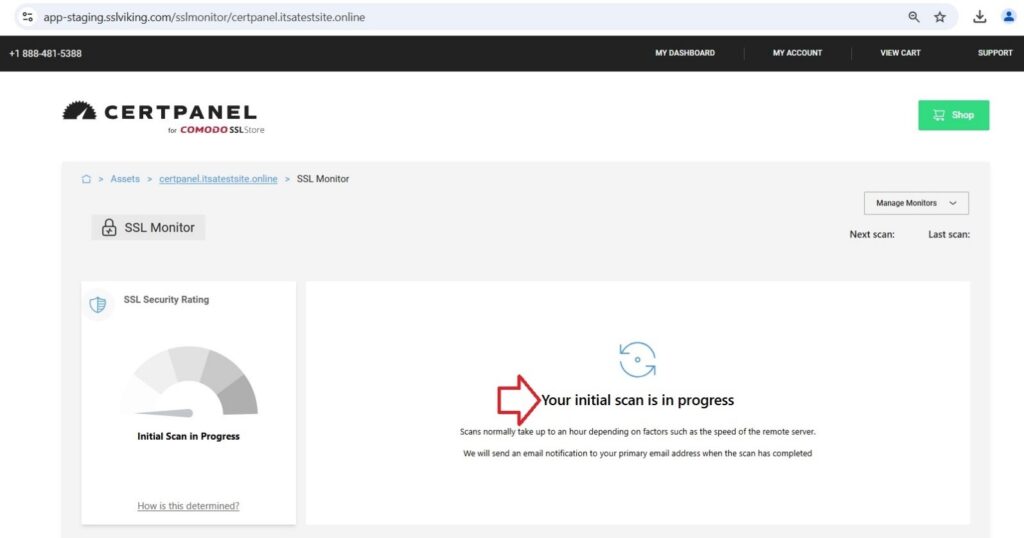
- Generate an SSL Scan: Under SSL Monitor, you will have the ability to scan your website. The tool will scan the suite of protocols regarding SSL/TLS on your website and report any vulnerabilities related to POODLE.
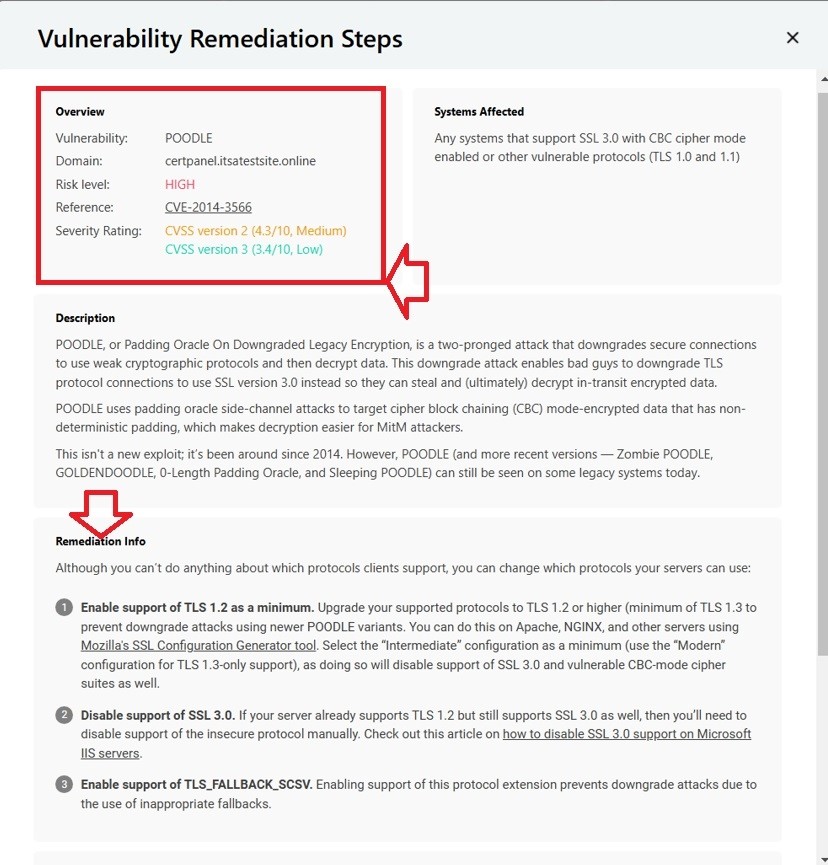
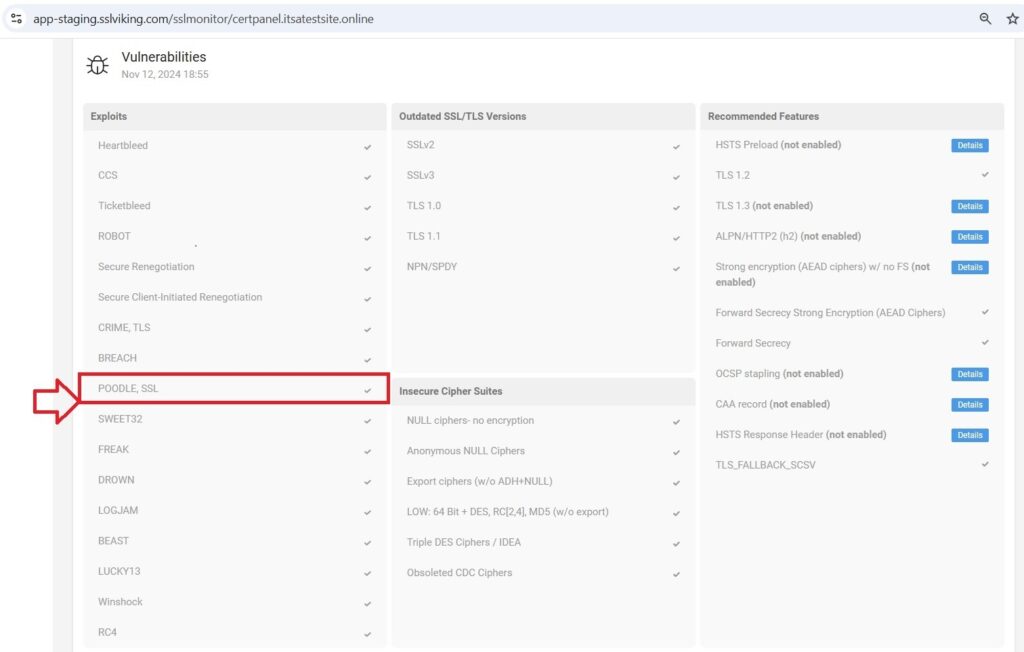
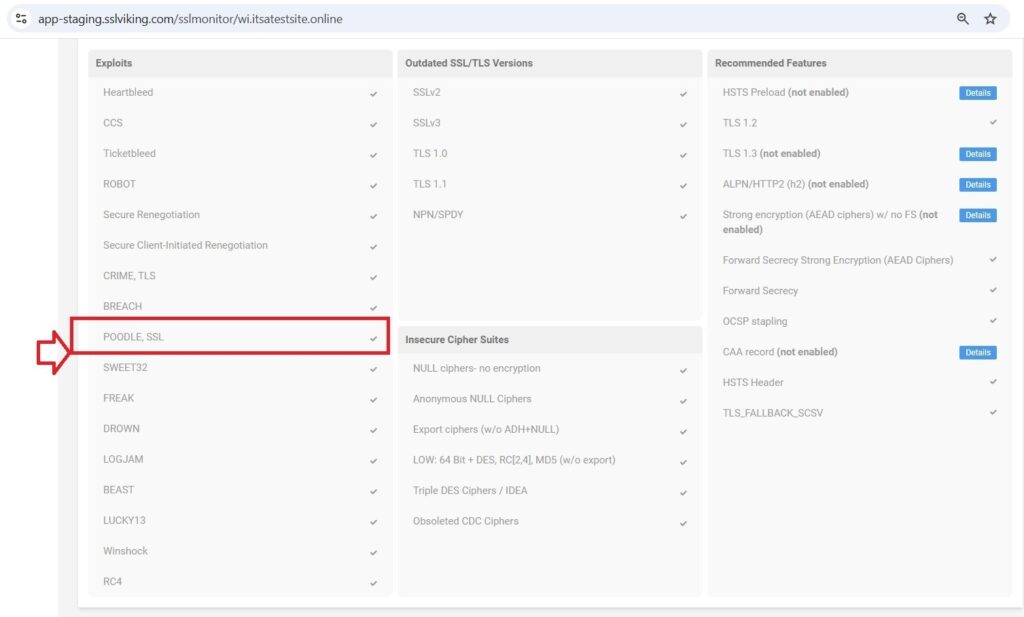
- Analyse Issues/ Mitigate Them: The results of the scan will show issues that need to be fixed. If SSL 3.0 shows as enabled, follow the steps to turn it off on your server using the following steps:
- Get Started with CertPanel SSL Monitor for proactive SSL security monitoring and POODLE protection.
Fixing SSL POODLE Vulnerability on Different Servers
1. Disabling SSL 3.0 on Ubuntu/Nginx
To disable the POODLE attack on Nginx servers, disable SSL 3.0 and enabling only TLS 1.2 or above.
Steps:
- Open the Virtual Host Configuration file:
# sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/default - Locate the ssl_protocols directive and edit to include only TLS 1.2 and above:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; - Restart Nginx:
# sudo service nginx restart - Run CertPanel SSL Monitor again to scan your server once more and ensure that SSL 3.0 has been disabled.
2. Disabling SSL 3.0 on Amazon Linux 2/Apache
Disabling SSL 3.0 in Apache servers running under Amazon Linux 2 would eliminate the POODLE vulnerability by adjusting the SSL configuration.
Steps:
- Open the SSL configuration file:
sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf - Change or add the SSLProtocol Directive to disable SSL 3.0:
# Protocols - Use Only TLS 1.2
SSLProtocol -all +TLSv1.2
# Updated Cipher Suites - Exclude Weak Ciphers
SSLCipherSuite ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:!CBC:!RC4:!SHA1:!3DES:!MD5:!LOW:!EXP:!aNULL:!eNULL
# Ensure the Server Honors the Cipher Order
SSLHonorCipherOrder On- Save the file and restart Apache:
# sudo systemctl restart httpd - Run an SSL Scan with CertPanel SSL Monitor to make sure SSL 3.0 is disabled.
3. Disabling SSL 3.0 on Windows Server (IIS)
To disable SSL 3.0 on IIS, you can modify the Windows Registry. This step is relevant for versions of Windows Server prior to 2019, as SSL 3.0 is disabled by default in Windows Server 2019 and later.
Steps:
- Open the Registry Editor by running ‘regedit’ from run box.
- Navigate to the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server
- If Server does not exist below SSL 3.0, then create it.
- Right-click on SSL 3.0, select New > Key, and name it Server if it doesn’t already exist.
- Inside the Server key, create a new DWORD (32-bit) Value named Enabled and set its value to 0 (which disables SSL 3.0).
- Finally, restart the server by running the following command from command prompt to apply the change.
Iisreset - To verify using CertPanel SSL Monitor that SSL 3.0 has been disabled on your IIS server.
How CertPanel SSL Monitor Streamlines Vulnerability Management
CertPanel SSL Monitor continuously monitors and alerts you in case the SSL 3.0 protocol is enabled or in the event of any other SSL/TLS weakness. In this way, keeping your protocols up to date and strong protects your website against POODLE attack or any such potential exploits.
The SSL POODLE attack (CVE-2014-3566) is a significant vulnerability that can compromise encrypted data on servers still supporting SSL 3.0. By disabling SSL 3.0 and using CertPanel SSL Monitor, you can proactively secure your site and provide a safer experience for users. Ensuring strong SSL/TLS protocols protects your website from outdated encryption vulnerabilities like POODLE, reinforcing trust and reliability.
- Get CertPanel SSL Monitor today for continuous SSL/TLS monitoring and security against POODLE and other vulnerabilities.